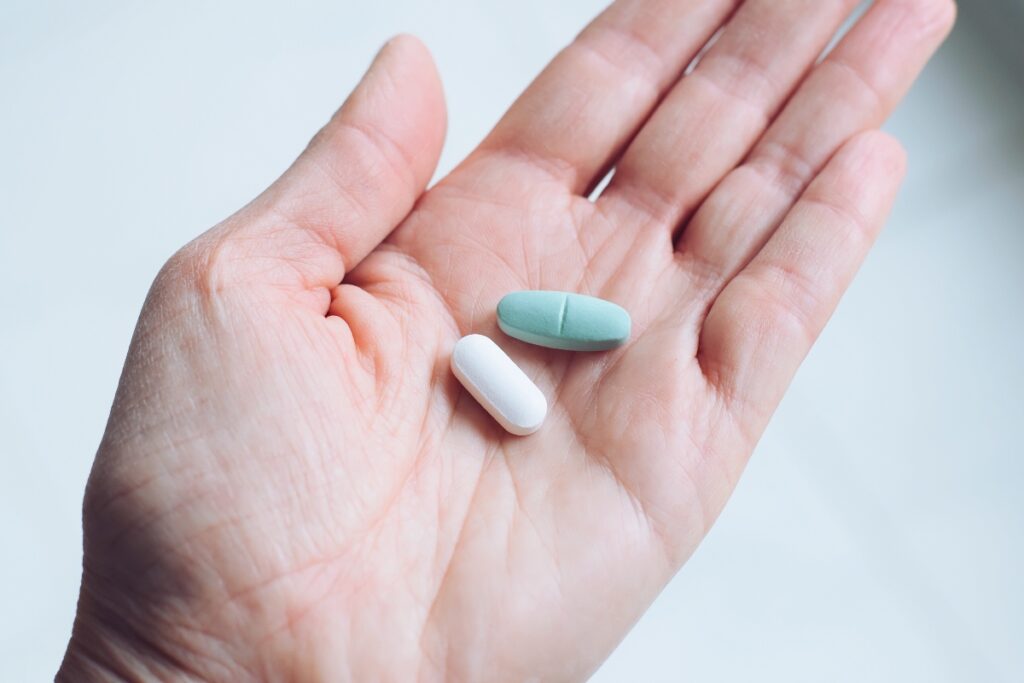
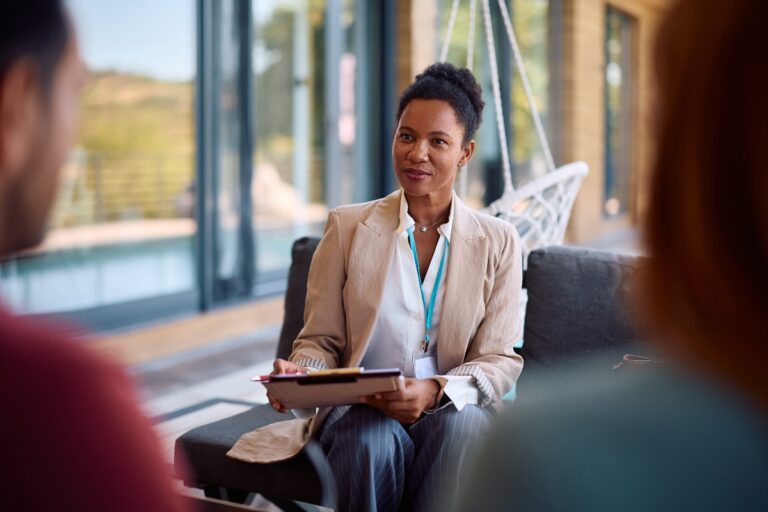
Prozac (brand name for fluoxetine) and Zoloft (brand name for sertraline hydrochloride) are both FDA-approved antidepressants that belong to the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) drug class. These prescription medications are commonly used to treat mental health conditions such as major depressive disorder (MDD), panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and social anxiety disorder. Though both medications increase serotonin levels in the brain to help improve mood, they differ in their chemical composition, half-life, and potential side effects.
One key difference between Prozac and Zoloft lies in their approved uses and pharmacokinetics. Prozac is often prescribed for bulimia nervosa, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, and major depression, and has a longer half-life, which can lead to fewer withdrawal symptoms. Zoloft, on the other hand, is frequently chosen for OCD, post-traumatic stress disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Additionally, individual responses to each medication vary, making it essential to consult a qualified healthcare provider or psychiatry specialist when determining which option best supports your well-being.
What is Prozac?
Prozac is the brand name for fluoxetine, a commonly prescribed antidepressant medication that belongs to the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) drug class. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Prozac is used to treat a range of mental health conditions, including major depressive disorder, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), bulimia nervosa, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Like other SSRIs, Prozac works by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, which can help improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Prozac is available in both capsule and oral solution forms, providing flexibility in treatment options. While it is generally well-tolerated, Prozac may cause some common side effects such as dry mouth, drowsiness, weight changes, and sexual dysfunction. It’s important to discuss any potential drug interactions or adverse effects with a healthcare provider, especially if taking other prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, or supplements. Always seek medical advice to determine whether Prozac is appropriate for your individual needs and mental health goals.
What Can Prozac Treat?
Prozac is a versatile antidepressant that is FDA-approved to treat a variety of mental health conditions. It is commonly used both as a first-line treatment and as part of combination therapy for individuals with mood and anxiety disorders. In some cases, healthcare providers may also prescribe Prozac off-label to address additional mental health symptoms or conditions.
Conditions Prozac can treat include:
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Bulimia nervosa
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (off-label)
- Generalized anxiety disorder (off-label)
- Social anxiety disorder (off-label)
- Treatment-resistant depression (often in combination with other therapies)
- Certain symptoms of bipolar disorder, when used with mood stabilizers (off-label)
Benefits of Taking Prozac
Prozac offers a number of advantages for individuals seeking relief from various mental health conditions. As one of the most well-researched and widely prescribed antidepressant drugs, Prozac provides a trusted treatment option for improving overall well-being and managing symptoms of depression and anxiety. It can be particularly effective for patients who have not responded to other antidepressant medications or are seeking a medication with a longer half-life.
Key benefits of taking Prozac include:
- FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, bulimia nervosa, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder
- Proven ability to increase serotonin levels, improving mood and reducing symptoms of depression
- Long half-life, which may result in fewer withdrawal symptoms if a dose is missed or when tapering off the medication
- Effective for treating treatment-resistant depression when used under the guidance of a healthcare provider
- Can help manage symptoms of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder (off-label use)
- Available in both capsule and oral solution forms for flexible dosing options
- Often used safely in adolescents and young adults under close medical supervision
Common Prozac Side Effects
Like all antidepressant medications, Prozac can cause side effects in some individuals. Most side effects are mild and tend to lessen as the body adjusts to the medication, but it’s important to be aware of potential reactions. Discuss any concerning symptoms with your healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective use of Prozac as part of your treatment plan.
Common side effects of Prozac include:
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness or fatigue
- Nausea and upset stomach
- Weight changes, including weight gain or weight loss
- Sexual dysfunction (such as decreased libido or difficulty achieving orgasm)
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- Increased sweating
- Headache
- Anxiety or nervousness
- Dizziness
In rare cases, more serious side effects—such as serotonin syndrome or heart rhythm disturbances—can occur. It’s essential to follow medical advice and report any adverse effects to your healthcare provider promptly.
What is Zoloft?
Zoloft is the brand name for sertraline, an antidepressant medication classified as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It is FDA-approved to treat a range of mental health conditions, including major depressive disorder, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), and social anxiety disorder. Like other SSRIs, Zoloft works by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, helping to regulate mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Zoloft is available in both tablet and oral solution forms, allowing for flexibility in dosing. It is often chosen for its proven efficacy and generally favorable side effect profile. However, like all antidepressant drugs, Zoloft can cause side effects such as dry mouth, drowsiness, sexual dysfunction, and gastrointestinal symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether Zoloft is an appropriate option based on your medical history, potential drug interactions, and individual mental health needs.
What Can Zoloft Treat?
Zoloft is a widely prescribed antidepressant used to treat a broad spectrum of mental health conditions. Its versatility and clinical effectiveness make it a first-line treatment option for various anxiety and mood disorders. While Zoloft is primarily FDA-approved for specific diagnoses, it may also be used off-label under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Conditions Zoloft can treat include:
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Social anxiety disorder
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
- Generalized anxiety disorder (off-label)
- Eating disorders such as binge eating (off-label)
- Symptoms of bipolar disorder when paired with mood stabilizers (off-label)
- Treatment-resistant depression (in combination with other antidepressant medications)
Benefits of Zoloft
Zoloft offers a number of advantages for individuals seeking relief from depression, anxiety, and related mental health conditions. It is one of the most commonly prescribed SSRIs and has a strong track record of safety and effectiveness. For many patients, Zoloft can significantly enhance quality of life and support long-term well-being.
Key benefits of taking Zoloft include:
- FDA-approved to treat major depressive disorder, PTSD, panic disorder, OCD, social anxiety disorder, and PMDD
- Proven to increase serotonin levels, helping to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety
- Effective for a wide range of mental health conditions and commonly used as a first-line treatment
- Available in both tablet and oral solution forms for flexible dosing
- Often well-tolerated with manageable side effects compared to older antidepressant drugs like tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Lower risk of weight gain compared to some other antidepressants
- May reduce symptoms of treatment-resistant depression when combined with other therapies
- Can be used safely in adolescents and young adults under medical supervision
Common Zoloft Side Effects
As with any antidepressant medication, Zoloft can cause side effects, especially when first starting treatment. Many side effects are mild and tend to resolve over time, but it is important to be aware of potential reactions. Always consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms that are bothersome or persistent.
Common side effects of Zoloft include:
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness or fatigue
- Nausea and upset stomach
- Sexual dysfunction (such as reduced libido or difficulty achieving orgasm)
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- Increased sweating
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea or gastrointestinal discomfort
- Weight changes (weight loss or, less commonly, weight gain)
In rare cases, Zoloft may cause more serious side effects, such as serotonin syndrome or changes in heart rhythm. It is essential to follow medical advice, report any adverse effects promptly, and never stop taking Zoloft abruptly without guidance to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
So Which Is Better?
When it comes to choosing between Prozac vs. Zoloft, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Both of these FDA-approved antidepressant medications are effective for treating a range of mental health conditions, including major depressive disorder, panic disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, differences in their side effect profiles, duration of action, and specific clinical uses may make one medication a better choice depending on the individual.
Prozac, with its longer half-life, may be preferable for patients concerned about withdrawal symptoms or those managing conditions like bulimia nervosa or premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Zoloft, on the other hand, is often favored for post-traumatic stress disorder, social anxiety disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder. Factors such as a patient’s unique symptom profile, potential drug interactions, and previous responses to antidepressant drugs should all be considered. Consulting a healthcare provider or psychiatry specialist is the best way to determine which medication is better suited to your personal mental health needs and well-being.
Find a Medication That Works for You
Deciding between Prozac vs. Zoloft—or any other antidepressant medications—ultimately depends on your individual needs, symptoms, and medical history. Both drugs have proven effective in treating a variety of mental health conditions, from major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder to obsessive-compulsive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder. However, factors like potential side effects, drug interactions, and personal response to treatment can vary greatly from one person to another.
If you’re considering starting or adjusting antidepressant therapy, it’s important to seek medical advice from a qualified healthcare provider. At Luxury Psychiatry Clinic, our experienced psychiatry team takes a personalized approach to mental health care, helping you navigate your treatment options and find a medication that supports your well-being. Whether you’re exploring SSRIs like Prozac and Zoloft or other advanced treatments such as TMS or ketamine therapy, we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and begin your journey toward improved mental health.